OSPFv2 Areas – OSPF, BGP, and Route Manipulation
As a network grows, the initial flooding and database maintenance of LSAs can burden a router’s CPU. OSPF uses areas to reduce these effects. An area is a logical grouping of routers and links that divides the network. Routers share link-state information with only the routers in their areas. This setup reduces the size of the database and the cost of computing the SPF tree at each router.
Using a topology with multiple areas provides the following benefits:
- The segmentation of the network reduces the number of SFP tree calculations.
- The segmentation of the network reduces the amount of LSA flooding.
- Multi-area design allows for summarization at the area border routers (ABRs).
- One OSPF area hides the topology from another area.
Each area is assigned a 32-bit integer number. Area 0 (or 0.0.0.0) is reserved for the backbone area. Every OSPF network should have a backbone area. The backbone area must exist in any internetwork using OSPF as a routing protocol over multiple areas. As you can see in Figure 4-2, communication between Area 1 and Area 2 must flow through Area 0. This communication can be internal to a single router that has interfaces directly connected to Areas 0, 1, and 2.
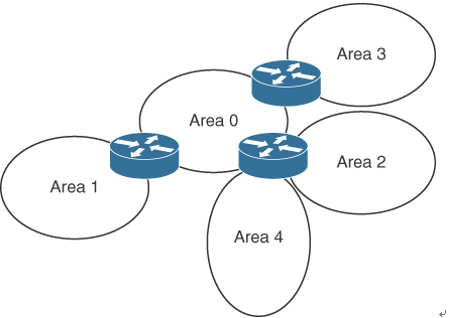
Figure 4-2 OSPF Areas
Intra-area traffic is packets passed between routers in a single area.
OSPF Area Design Considerations
A CCNP enterprise designer should be aware of a few considerations in the design of OSPF areas. First, in a hub-and-spoke design, you have a remote branch keep the OSPF boundary at the hub side, as shown in Figure 4-3. This allows the branch router to calculate SPF only within its own area and limits the LSA flooding. If the OSPF Area 0 boundary were extended to the branch, the branch router would have to do OSPF calculations for Area 0 and its own area, and LSAs would flood over the WAN link.
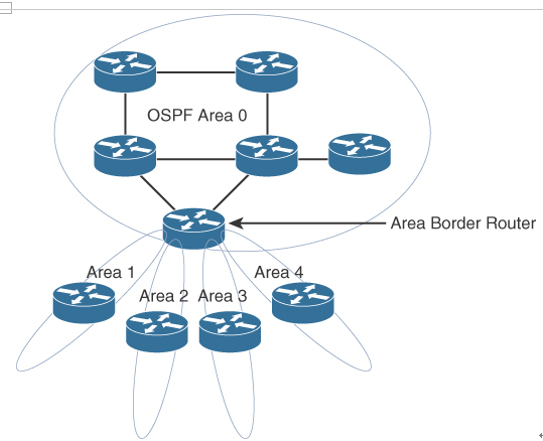
Figure 4-3 OSPF Area Design
The second design consideration is to avoid grouping remote branches into a single area. Having all remote branches in the same area is not scalable. Instead, place each remote branch in its own area to limit LSA flooding and SPF recalculations.
