Next-Hop Attribute – OSPF, BGP, and Route Manipulation
The next-hop attribute is the IP address of the next IP hop that will be used to reach the destination. The next-hop attribute is a well-known mandatory attribute.
Local Preference Attribute
The local preference attribute indicates which path to use to exit the autonomous system. It is a well-known discretionary attribute used between iBGP peers and is not passed on to external BGP peers. In Cisco IOS software, the default local preference is 100. The higher local preference is preferred.
The default local preference is configured on the BGP router with an external path; it then advertises its local preference to internal iBGP peers. Figure 4-14 shows an example of the local preference attribute where Routers B and C are configured with different local preference values. Router A and other iBGP routers then receive routes from both Router B and Router C. Between the two possible paths (shown with arrows), Router A prefers using Router C to route Internet packets because it has a higher local preference (400) than Router B (300).
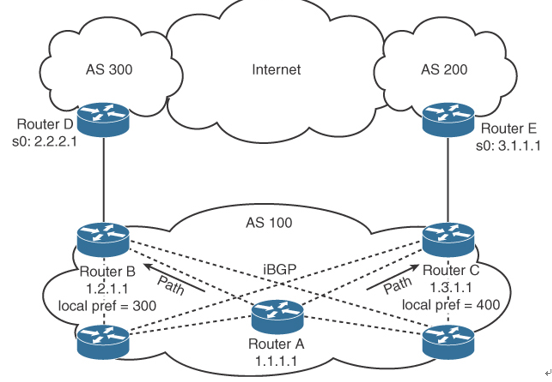
Figure 4-14 BGP Local Preference
Origin Attribute
Origin is a well-known mandatory attribute that defines the source of the path information. Do not confuse the origin with comparing whether a route is external (eBGP) or internal (iBGP). The origin attribute is received from the source BGP router. There are three types:
- IGP: Indicated by an i in the BGP table. Present when the route is learned by way of the network statement.
- EGP: Indicated by an e in the BGP table. Learned from an EGP peer.
- Incomplete: Indicated by a question mark (?) in the BGP table. Learned from redistribution of the route.
In terms of choosing a route based on origin, BGP prefers routes that have been verified by an IGP over routes that have been learned from EGP peers, and BGP prefers routes learned from eBGP peers over incomplete paths.
Autonomous System Path (AS_Path) Attribute
The autonomous system path is a well-known mandatory attribute that contains a list of ASNs in the path to the destination. Each autonomous system prepends its own ASN to the autonomous system path. The autonomous system path describes all the autonomous systems a packet would have to travel to reach the destination IP network. It is used to ensure that the path is loop free. When the AS_Path attribute is used to select a path, the route with the fewest autonomous system hops is preferred. In the case of a tie, other attributes, such as MED, break the tie. Example 4-1 shows the autonomous system path for network 200.50.32.0/19. To reach the destination, a packet must pass autonomous systems 3561, 7004, and 7418. The command show ip bgp 200.50.32.0 displays the autonomous system path information.
Example 4-1 Autonomous System Path Attribute
Click here to view code image Router#
show ip bgp 200.50.32.0
BGP routing table entry for 200.50.32.0/19, version 93313535
Paths: (1 available, best #1)
Not advertised to any peer
3561 7004 7418
206.24.241.181 (metric 490201) from 165.117.1.219 (165.117.1.219)
Origin IGP, metric 4294967294, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Community: 2548:182 2548:337 2548:666 3706:153
