MED Attribute – OSPF, BGP, and Route Manipulation
The multi-exit discriminator (MED) attribute tells an external BGP peer the preferred path into the autonomous system when multiple paths into the same autonomous system exist. In other words, MED influences which one of many paths a neighboring autonomous system uses to reach destinations within the autonomous system. It is an optional nontransitive attribute carried in eBGP updates. The MED attribute is not used with iBGP peers. The lowest MED value is preferred, and the default value is 0. Paths received with no MED are assigned a MED of 0. The MED is carried into an autonomous system but does not leave the autonomous system.
Consider the diagram shown in Figure 4-15. With all attributes considered equal, say that Router C selects Router A as its best path into AS 100, based on Router A’s lower router ID (RID). If Router A is configured with a MED of 200, Router C will select Router B as the best path to AS 100. No additional configuration is required on Router B because the default MED is 0.
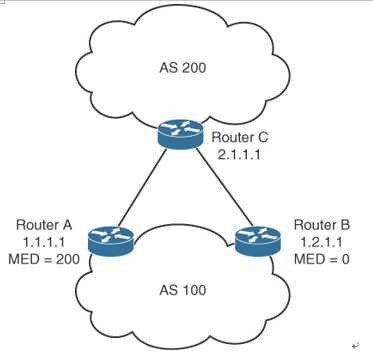
Figure 4-15 MED Attribute
Community Attribute
Although it is not an attribute used in the routing-decision process, the community attribute groups routes and applies policies or decisions (accept, prefer) to those routes. It is a group of destinations that share some common property. The community attribute is an optional transitive attribute of variable length.
Atomic Aggregate and Aggregator Attributes
The atomic aggregate attribute informs BGP peers that the local router used a less specific (aggregated) route to a destination instead of using a more specific route.
The purpose of the attribute is to alert BGP speakers along the path that some information has been lost due to the route aggregation process, and the aggregate path might not be the best path to the destination. When some routes are aggregated by an aggregator, the aggregator does attach its RID to the aggregated route in the AGGREGATOR_ID attribute, and it sets the ATOMIC_AGGREGATE attribute (or not) based on whether the AS_Path information of the aggregated routes was preserved. The atomic aggregate attribute lets the BGP peers know that the BGP router used an aggregated route. A more specific route must be in the advertising router’s BGP table before it propagates an aggregate route.
When the atomic aggregate attribute is used, the BGP speaker has the option to send the aggregator attribute. The aggregator attribute includes the ASN and the IP address of the router that originated the aggregated route. In Cisco routers, the IP address used is the RID of the router that performs the route aggregation. Atomic aggregate is a well-known discretionary attribute, and aggregator is an optional transitive attribute.
