IP Multicast Review – IP Multicast and Network Management
With multicast, packets are sent to a multicast group, which is identified with an IP multicast address. Multicast supports the transmission of IP packets from one source to multiple hosts. Packets with unicast addresses are sent to one device, and broadcast addresses are sent to all hosts; packets with multicast addresses are sent to a group of hosts.
Multicast Addresses
Multicast addressing uses Class D addresses from the IPv4 protocol. Class D addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages multicast addresses.
Routing protocols (such as RIPv2, EIGRP, and OSPF) use multicast addresses to speak to their neighbors. For example, OSPF routers use 224.0.0.6 to speak to the designated router (DR) in a multiaccess network. Class D multicast addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. Multicast addresses in the range 224.0.0.1 to 224.255.255.255 are reserved for special addresses or network protocols on a multiaccess link. RFC 2365 reserves multicast addresses in the range 239.192.000.000 to 239.251.255.255 for organization-local scope. Similarly, 239.252.000.000 to 239.252.255.255, 239.254.000.000 to 239.254.255.255, and 239.255.000.000 to 239.255.255.255 are reserved for site-local scope.
Table 5-2 lists some well-known and multicast address blocks.
Table 5-2 Multicast Addresses
| Multicast Address | Description |
| 224.0.0.0/24 | Local network control block |
| 224.0.0.1 | All hosts or all systems on the subnet |
| 224.0.0.2 | All multicast routers |
| 224.0.0.4 | Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) routers |
| 224.0.0.5 | All OSPF routers |
| 224.0.0.6 | All OSPF DR routers |
| 224.0.0.9 | RIPv2 routers |
| 224.0.0.10 | EIGRP routers |
| 224.0.0.13 | All PIM routers |
| 224.0.1.0/24 | Internetwork control block |
| 224.0.1.39 | Rendezvous point (RP) announcement |
| 224.0.1.40 | RP discovery |
| 224.0.2.0 to 224.0.255.0 | Ad hoc block |
| 239.000.000.000 to 239.255.255.255 | Administratively scoped |
| 239.192.000.000 to 239.251.255.255 | Organization-local scope |
| 239.252.000.000 to 239.254.255.255 | Site-local scope |
Layer 3 to Layer 2 Mapping
Multicast-aware Ethernet, Token Ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) network interface cards use the reserved IEEE 802 address 0100.5e00 for multicast addresses at the MAC layer. This includes Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. Notice that for the address, the high-order byte 0x01 has the low-order bit set to 1. This bit is the Individual/Group (I/G) bit, and it signifies whether the address is an individual address (0) or a group address (1). Hence, for multicast addresses, this bit is set to 1.
Ethernet interfaces map the lower 23 bits of the IP multicast address to the lower 23 bits of the MAC address 0100.5e00.0000. As an example, the IP multicast address 224.0.0.2 is mapped to the MAC layer as 0100.5e00.0002. Figure 5-1 shows another example, looking at the bits of multicast IP address 239.192.44.56, which in hexadecimal is EF:C0:2C:38. The lower 23 bits get mapped to the lower 23 bits of the base multicast MAC to produce the multicast MAC address 01:00:5E:40:2C:38.
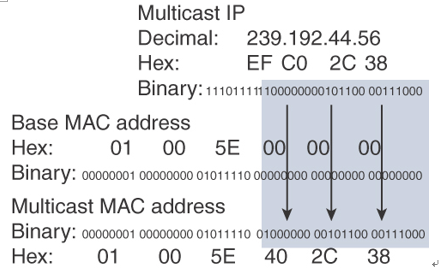
Figure 5-1 Mapping of Multicast IP Addressing to MAC Addresses
